Modulation -concept,advantages,classification,analog & digital modulation
What is modulation?
·
Operation of varying amplitude,
frequency or phase of carrier signal accordingly with the instantaneous
amplitude of the message signal is called modulation
·
Modulation= Adding information to a
carrier signal
Need for Modulation:
Baseband signals are incompatible for
direct transmission. For such a signal, to travel longer distances, its
strength has to be increased by modulating with a high frequency carrier wave,
which doesn’t affect the parameters of the modulating signal.
Advantages of Modulation
The antenna used for
transmission, had to be very large, if modulation was not introduced. The range
of communication gets limited as the wave cannot travel a distance without
getting distorted.
Following are some of
the advantages for implementing modulation in the communication systems.
- Reduction of antenna size
- No signal mixing
- Increased communication
range
- Multiplexing of signals
- Possibility of bandwidth
adjustments
- Improved reception quality
v
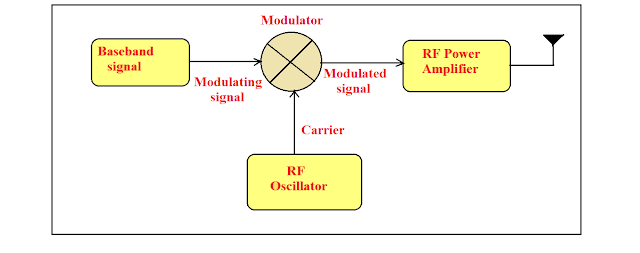
Signals in the Modulation Process
Following are the three types of signals in the modulation process.
Message or Modulating
Signal
The signal which contains a message to be transmitted, is called as
a message signal. It is a baseband signal, which has to undergo the
process of modulation, to get transmitted. Hence, it is also called as the modulating
signal.
Carrier Signal
The high frequency signal, which has a certain amplitude, frequency and
phase but contains no information is called as a carrier signal. It
is an empty signal and is used to carry the signal to the receiver after modulation.
Modulated Signal
The resultant signal after the process of modulation is called as
a modulated signal. This signal is a combination of modulating
signal and carrier signal.
v
Types of Modulation
There are many types of modulations. Depending upon the modulation
techniques used, they are classified as shown in the following figure.
Continuous-wave Modulation
In continuous-wave
modulation, a high frequency sine wave is used as a carrier wave. This is
further divided into amplitude and angle modulation.
·
If the amplitude of the high frequency carrier wave is varied in
accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal, then such
a technique is called as Amplitude Modulation.
·
If the angle of the carrier wave is varied, in accordance with the
instantaneous value of the modulating signal, then such a technique is called
as Angle Modulation. Angle modulation is further divided into frequency
modulation and phase modulation.
o
If the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, in accordance with the
instantaneous value of the modulating signal, then such a technique is called
as Frequency Modulation.
o
If the phase of the high frequency carrier wave is varied in accordance
with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal, then such a technique is
called as Phase Modulation.
Pulse Modulation
In Pulse modulation,
a periodic sequence of rectangular pulses, is used as a carrier wave. This is
further divided into analog and digital modulation.
In analog modulation
technique, if the amplitude or duration or position of a pulse is varied in
accordance with the instantaneous values of the baseband modulating signal,
then such a technique is called as Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) or Pulse
Duration/Width Modulation (PDM/PWM), or Pulse Position Modulation (PPM).
In digital
modulation, the modulation technique used is Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) where
the analog signal is converted into digital form of 1s and 0s. As the resultant
is a coded pulse train, this is called as PCM. This is further developed as
Delta Modulation (DM). These digital modulation techniques are discussed in our
Digital Communications tutorial
Another way
·
Analog modulation:
If the variation in the parameter of the carrier is continuous in
accordance to the input analog signal the modulation technique is termed as
analog modulation scheme. It is classified as:
1.
Amplitude Modulation
2.
Frequency Modulation
3.
Phase Modulation
·
Digital Modulation:
If the variation in
the parameter of the carrier is discrete then it is termed as digital
modulation technique.it is classified as:
1.
Amplitude Shift Keying
2.
Frequency Shift Keying
3.
Phase shift keying









Thank you sir.. this post is very useful for me
ReplyDeletegreat post..
ReplyDelete